Table of contents
- 1 Introduction
- 1.1 Inspiration for Book module redesign
- 1.2 Why fork the existing Book module?
- 1.3 Why is it called "Interactive" book?
- 2 New features and improvements
- 2.1 Modern look and feel
- 2.2 Improved book structure, layout and navigation
- 2.3 New content types
- 2.4 Major security improvements
- 2.5 Improved printing support
- 2.6 Hidden chapters replaced by hidden content
- 2.7 Full support for Markdown text format
- 2.8 Removed features
- 3 Content types
- 3.1 HTML text
- 3.2 Unsafe raw HTML
- 3.3 Markdown text
- 3.4 Solution disclosure button
- 3.5 Content ideas
- 4 Markdown support
- 4.1 Why Markdown?
- 4.2 Basic Markdown formatting
- 4.3 Images and attachments
- 4.4 GitHub Flavored Markdown
- 5 Future development
- 5.1 Production release plan
- 5.2 Other ideas
1 Introduction
The Interactive book plugin is the successor to original Book module in Moodle™ LMS, offering enhanced functionality and a more dynamic learning experience.
1.1 Inspiration for Book module redesign
The Book module has been a staple in Moodle for creating multi-page resources that resemble digital textbooks. It’s simple and familiar, but it comes with a few limitations that are worth knowing.
Security is one of the biggest concerns. Students should never be allowed to edit books, because doing so could allow them to gain access to administrator accounts. The module is also quite static - it doesn’t support interactive elements like quizzes or embedded activities directly, though you can link to them externally. Tracking learner progress is tricky too, since the Book module doesn’t connect to any learning analytics tools. And if you’ve ever deleted a chapter with subchapters, you’ll know how easy it is to lose content - there’s no version control to help recover it.
There are also some persistent issues that users often mention. Navigating between chapters can feel awkward, especially in longer books or those with multimedia. Styling is another challenge - because content is written in HTML, it’s hard to keep a consistent look across different courses. And perhaps most telling, Moodle HQ hasn’t added any new features to the Book module in over a decade.
At MoodleMoot DACH 2025, hosted at Technische Hochschule Lübeck, the Book module came up in several participant-led discussions. I was genuinely surprised to discover how many people still rely on the Book module every single day to create content for their students. It’s clearly more alive - and more widely used - than I ever expected.
1.2 Why fork the existing Book module?
The Book module in Moodle has been around for over 20 years, and it’s starting to show its age. The way it’s built makes it hard to improve, and the design feels outdated. Navigating between chapters can be frustrating, and the overall experience doesn’t match what today’s learners and teachers expect.
There’s also a serious safety concern. Right now, anyone who can edit a Book can add code that might harm other users or the site. This makes it risky to use in courses where students are contributing content.
One way to fix this would be to rethink how Books are built. Instead of each chapter being a big block of content, we could break it into smaller, safer pieces and let teachers use secure widgets to add interactive elements - without needing to copy and paste code from random websites.
But doing that properly would mean changing how the Book module stores and handles content behind the scenes. The old system just isn’t built for that, and trying to migrate data of existing Books automatically could cause more problems than it solves.
That’s why creating a brand-new Book module makes sense. It gives developers the freedom to try new ideas, improve the experience, and keep things secure - without breaking the old Books that people are still using. Both versions can exist side by side, so schools can switch over when they’re ready or where appropriate.
1.3 Why is it called "Interactive" book?
The key differences from the original Book module in Moodle are improved usability, enhanced security, and interactivity. Of those, only one truly sparks excitement - so Interactive book plugin it is!
Tip
Right now, it comes with just one interactive feature - “Show solution button”. Think of it as a digital peekaboo for answers. But don’t worry - this is just the opening chapter. More interactive goodies are on the way soon, and they’ll be much more exciting than hiding and revealing text (though we admit, that’s oddly satisfying too).
2 New features and improvements
The updates to the Interactive Book module go beyond visual improvements. Changes to both its internal structure and user interface are designed to support future enhancements and make it easier to introduce new features over time. This foundation helps ensure the module can evolve with the needs of educators and learners, while maintaining a smoother and more flexible experience.
2.1 Modern look and feel
2.2 Improved book structure, layout and navigation
2.3 New content types
2.4 Major security improvements
2.5 Improved printing support
2.6 Hidden chapters replaced by hidden content
2.7 Full support for Markdown text format
2.8 Removed features
3 Content types
Interactive book chapters are made up of individual content blocks, giving authors flexibility to structure their material. Right now, only a few content types are available, but more will be implemented soon.
3.1 HTML text
3.2 Unsafe raw HTML
3.3 Markdown text
3.4 Solution disclosure button
3.5 Content ideas
4 Markdown support
Markdown is a lightweight markup language that makes it easy to format text using plain characters. It's widely used for writing books, documentation, and educational content because it's simple, readable, and portable.
4.1 Why Markdown?
Markdown is especially well-suited for writing books because it keeps the focus on content, not formatting. Its clean, readable syntax lets authors structure chapters, headings, lists, and links without the distraction of HTML tags or complex styling. This simplicity makes it easier to write, edit, and collaborate- especially in educational settings where clarity and consistency matter.
For educators creating course books, Markdown offers a fast and reliable way to produce structured content that can be easily converted to HTML, PDF, or other formats. It also works well with version control, making it ideal for tracking changes or co-authoring materials. Because Markdown is plain text, it’s future-proof and portable - your content isn’t locked into any one platform or editor.
In short, Markdown helps educators write better books by making the process smoother, cleaner, and more focused on what really matters: the ideas.
4.2 Basic Markdown formatting
Markdown is designed to be easy to write and easy to read. Instead of using complex HTML tags, you format text with plain symbols like #, *, and -. This makes it ideal for authors, educators, and developers who want to focus on content rather than layout.
The Interactive book module follows the CommonMark standard - a widely adopted Markdown specification that ensures consistent behavior across platforms.
If you're new to Markdown or just want a quick refresher, the CommonMark tutorial is a great place to start. It walks you through the basics step by step, with examples you can try out right away.
Headings
Use # for headings. More # symbols mean deeper levels.
# Chapter Title
## Section Title
### Subsection Title
Tip
Interactive book module alters the heading level automatically to match current page to improve the content accessibility.
Emphasis
Use asterisks or underscores for italics and bold.
*italic text*
**bold text**
***bold and italic***
- italic text
- bold text
- bold and italic
Lists
Create bullet or numbered lists.
- First item
- Second item
1. Step one
2. Step two
- First item
- Second item
- Step one
- Step two
Links
Use square brackets for the link text and parentheses for the URL.
[Visit Moodle](https://moodle.org)
Images
Add images using an exclamation mark before the link.

Blockquotes
Use > to create a blockquote.
> This is a quoted paragraph.
This is a quoted paragraph.
Horizontal Line
Use three dashes or asterisks to create a horizontal line.
---
Escaping Characters
Use a backslash \ to escape Markdown symbols.
\*This will not be italic\*
*This will not be italic*
Code
Use backticks for inline code and triple backticks for code blocks.
Inline example: `print("Hello")`
Inline example: print("Hello")
Use three backticks ``` for blocks of code.
```
def greet(): print("Hello, world!")
```
def greet(): print("Hello, world!")
4.3 Images and attachments
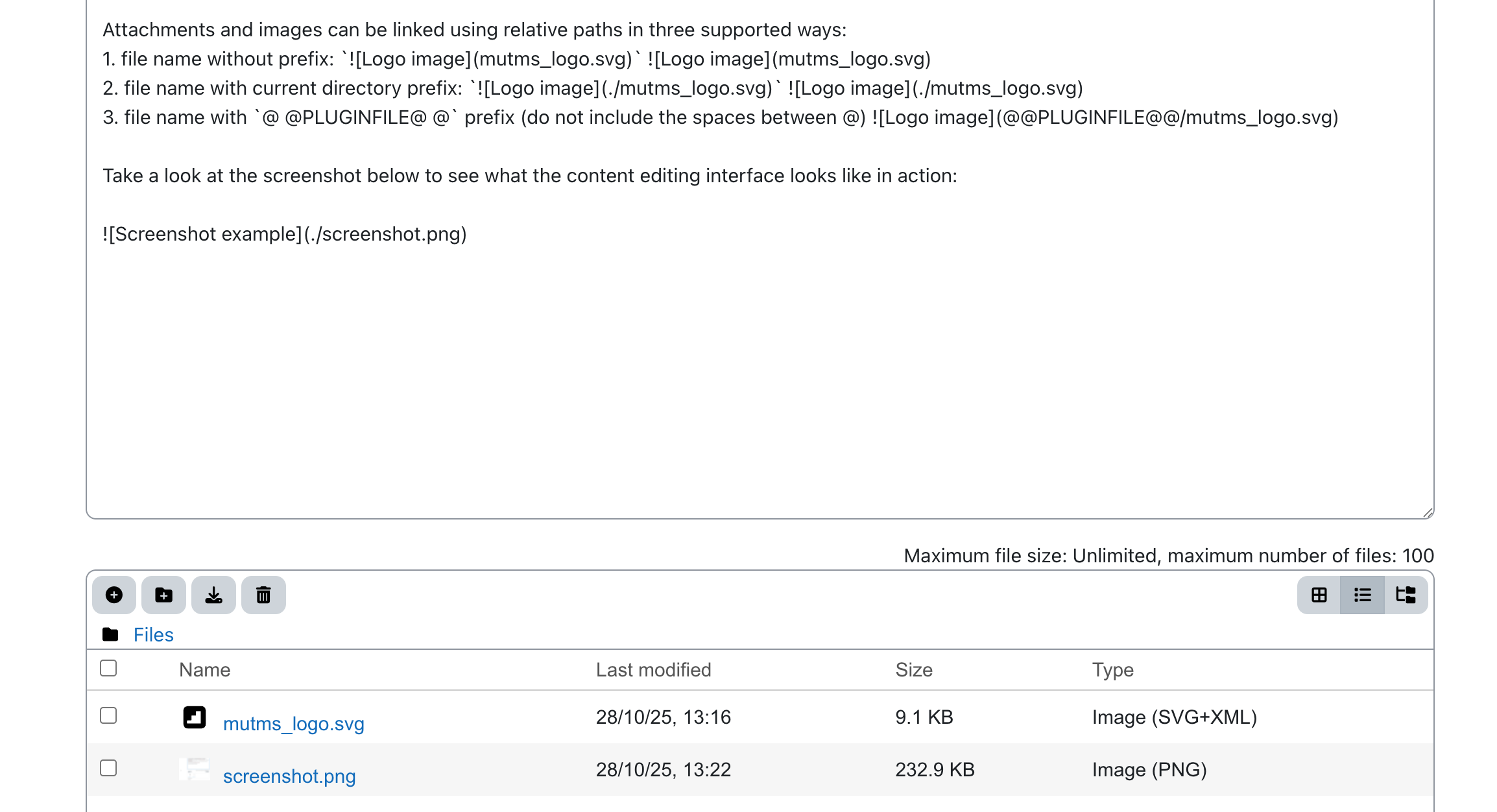
To create a fully self-contained book, you can add attachments and images directly to each Markdown content block. This allows all resources to stay bundled with the book, making it easier to share, archive, or reuse without external dependencies.
Attachments and images can be linked using relative paths in three supported ways:
- file name without prefix:
 - file name with current directory prefix:
 - file name with
@ @PLUGINFILE@ @prefix (do not include the spaces between @)
Take a look at the screenshot below to see what the content editing interface looks like in action:
4.4 GitHub Flavored Markdown
GitHub Flavored Markdown (GFM) builds on the CommonMark standard, but adds practical features that make it especially well-suited for writing educational books - particularly when those books are collaborative or include technical content.
Interactive books currently support a limited subset of GitHub Flavored Markdown (GFM).
Tables for structured content
GFM supports native table syntax, which CommonMark does not. This is essential for educators who need to present data, comparisons, or structured information clearly.
| Term | Definition |
|------------|--------------------|
| Markdown | Lightweight markup |
| GFM | Extended Markdown |
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Markdown | Lightweight markup |
| GFM | Extended Markdown |
Use ~~ to strike through text
~~This is outdated~~
This is outdated
Alerts
> [!NOTE]
> This is a note.
> [!TIP]
> This is just a tip.
> [!IMPORTANT]
> Some things are really important.
> [!WARNING]
> You are being warned!
> [!CAUTION]
> Be cautious!
Note
This is a note.
Tip
This is just a tip.
Important
Some things are really important.
Warning
You are being warned!
Caution
Be cautious!
Task list
- [ ] foo
- [x] bar
- foo
- bar
MathJax embedding
To include inline mathematical notation use backtick with single dollar wrapping, for example \(ax^2 + bx + c = 0\) is entered as
for example $`ax^2 + bx + c = 0`$ is entered as
To include a mathematical notation in a block use ```math code block:
```math
x = {-b \pm \sqrt{b^2-4ac} \over 2a}
```
5 Future development
The Interactive Book module is already functional and shaping up nicely - most features are working as expected. While it’s not quite production-ready yet, we’re getting closer every day!
If you’d like to explore it early, now’s a great time to jump in and help shape its future.